Collaboration
Observable Canvases are designed as a space where people can talk over their data in diverse ways. Some may be writing SQL; some may be sculpting queries with visual interfaces; some may be taking notes, diagramming, or just pointing to something that looks surprising.
Permissions
Canvases can be private or shared within your workspace. You can either share a canvas with the whole team (the default for new canvases), or you can share with individuals or groups.
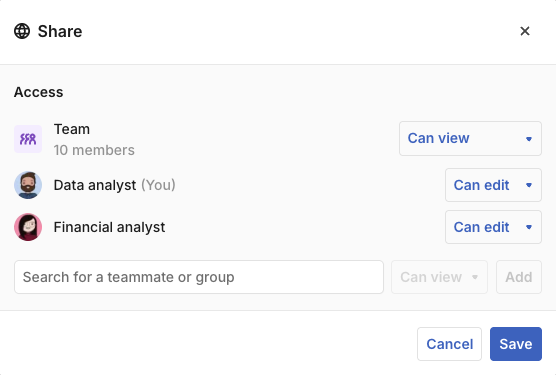
You can also select your permissions when you create a new canvas:
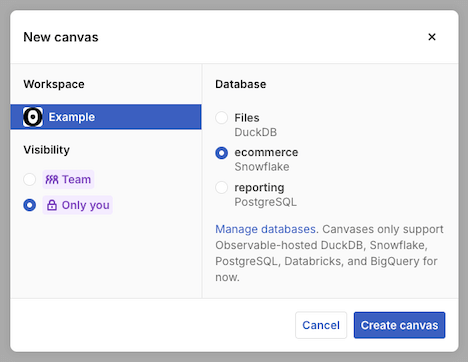
When a workspace has edit access to a canvas, any editor in the workspace can edit it. Workspace members with a “viewer” role can only see the canvas in presentation mode; they can interact with the canvas to adjust filters and brushes, but no edits will be saved. Guest editors and guest viewers cannot access canvases at all.
For sharing your work with a broader audience, see sharing.
Multiplayer
Your canvas is synchronized in real-time with other editors. You can see each other’s:
- Cursor positions
- Notes, doodles, and other whiteboarding
- Nodes and edges
- Filters and brushes
- AI-generated outputs
Query snapshots
When lots of people are looking at the canvas at the same time, you don’t want lots of redundant queries hammering your database. Canvases run each query exactly once (until updated or manually run again); everyone else sees a cached snapshot of the results, for fast exploration that scales to your whole team. To learn more, see data sources.
What’s not synchronized
Some aspects of the canvas are not synchronized in real-time:
- Text and code - these only update for others when you blur the node; they will see only your selection outline on the node
- Node control tabs - e.g., if you switch from the “Settings” tab to the “Columns” tab, others won’t see it change
- Table scrolling - e.g., if you scroll a table and hover over a specific row or column, others will see your multiplayer cursor over a different part of the table, depending on how they’ve scrolled it
- Files uploaded to a DuckDB canvas - others will have to refresh the page to see them
Detached mode
If you are viewing a presentation link, or if you have a viewer role in the workspace, you will see the canvas in “detached mode”. You can still interact with filters and brushes, but your changes will not be saved. You will not see others’ edits live, and they will not see yours.
WARNING
Viewers in detached mode can still run any query against your data source that a canvas editor could run, including queries the original editors may not have expected. Detached mode is not a security feature for restricting access to your data; it only protects against saving changes to the canvas.
Tools
There are a few tools that don’t make lasting edits to the canvas, but do help you collaborate in it.
Following
Click the profile pictures in the upper right of the canvas to see a list of the people currently editing the canvas. (Viewers in detached mode do not appear here.) Click someone’s name to jump to their current position. Click the eye icon to follow them; the eye will look to the left . An eye looking to the right indicates someone who is following you.
Cursor chat
Right-click the canvas and click “Cursor chat” or press the slash key (/) to begin writing a message for cursor chat. Other canvas editors will see your message over your cursor.
Lasers
The laser tool (K) lets you point at things on the canvas without editing them. It leaves a trail that quickly fades to highlight its movement.