JavaScript nodes
WARNING
JavaScript nodes are experimental and subject to change.
JavaScript nodes execute an expression or function body and render the result as either a DOM node or an inspector. They take one input node. Create a JavaScript node by selecting an existing node and clicking New JavaScript node on the new node toolbar floating to the right.
Configuration
Unlike other nodes, the JavaScript node does not configure a query for other nodes to consume; it just runs the code and renders the result. The code can be an expression:
input.lengthOr a function body with a return statement:
const len = input.length;
return len;If the return value is a DOM node, it will be rendered. Otherwise, the value will be shown using the inspector.
The code runs with three special variables defined:
input- the first 100,000 rows of the input query resultsPlot- the Observable Plot libraryd3- the D3 library
Example
First we’ll load some data. On a DuckDB canvas, create a SQL node that loads a list of recent earthquakes from the USGS website:
SELECT longitude, latitude, mag
FROM 'https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/2.5_week.csv'From that node, create a JavaScript node and inspect input:
return input;Find the earthquake with the largest magnitude:
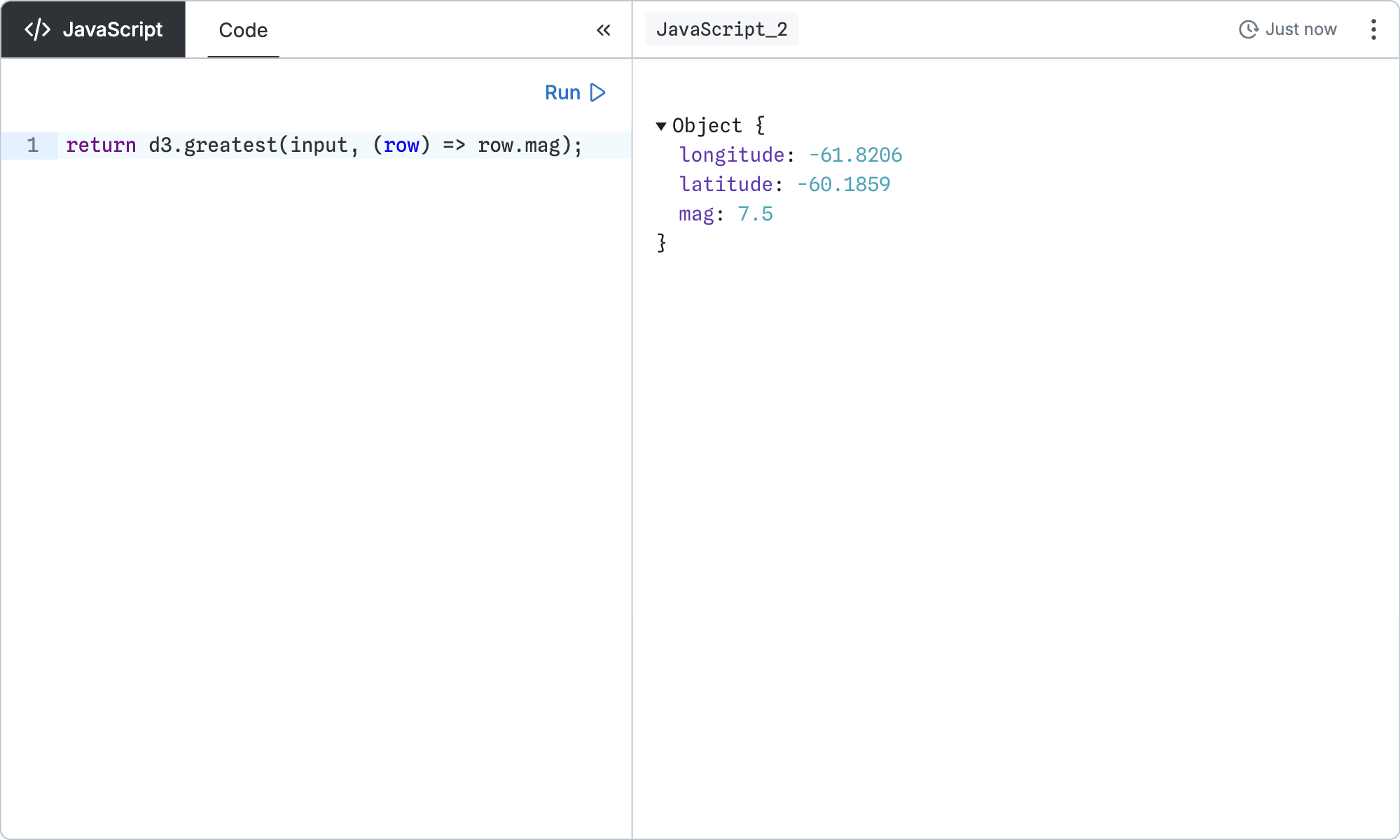
return d3.greatest(input, (row) => row.mag);Display a scatterplot of earthquakes’ longitude and latitude:
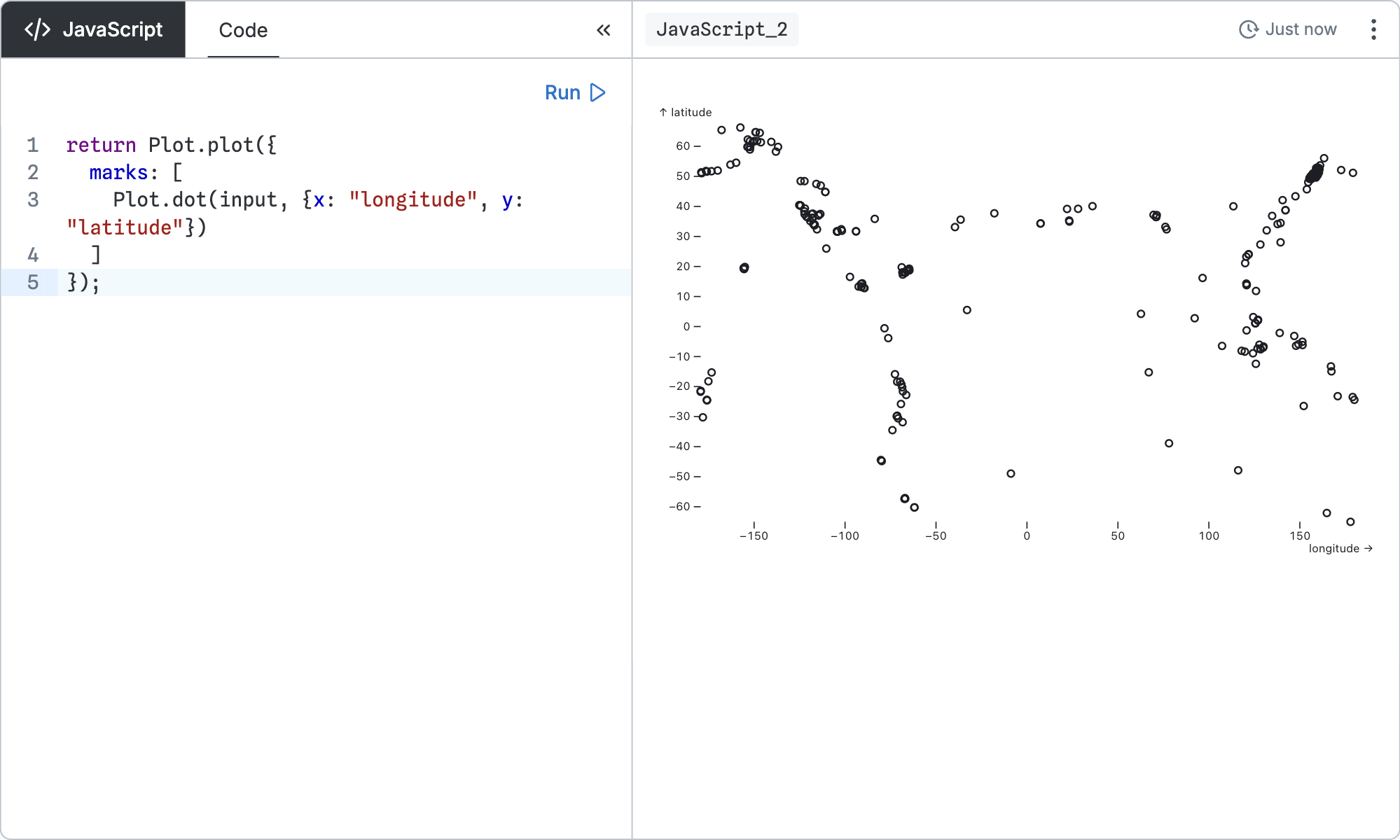
return Plot.plot({
marks: [
Plot.dot(input, {x: "longitude", y: "latitude"})
]
});The program runs synchronously. However, you can return a placeholder element and update it asynchronously.
For example, to draw a map of earthquakes, you can asynchronously load the topojson library and a base map, then append a Plot map to the placeholder element:
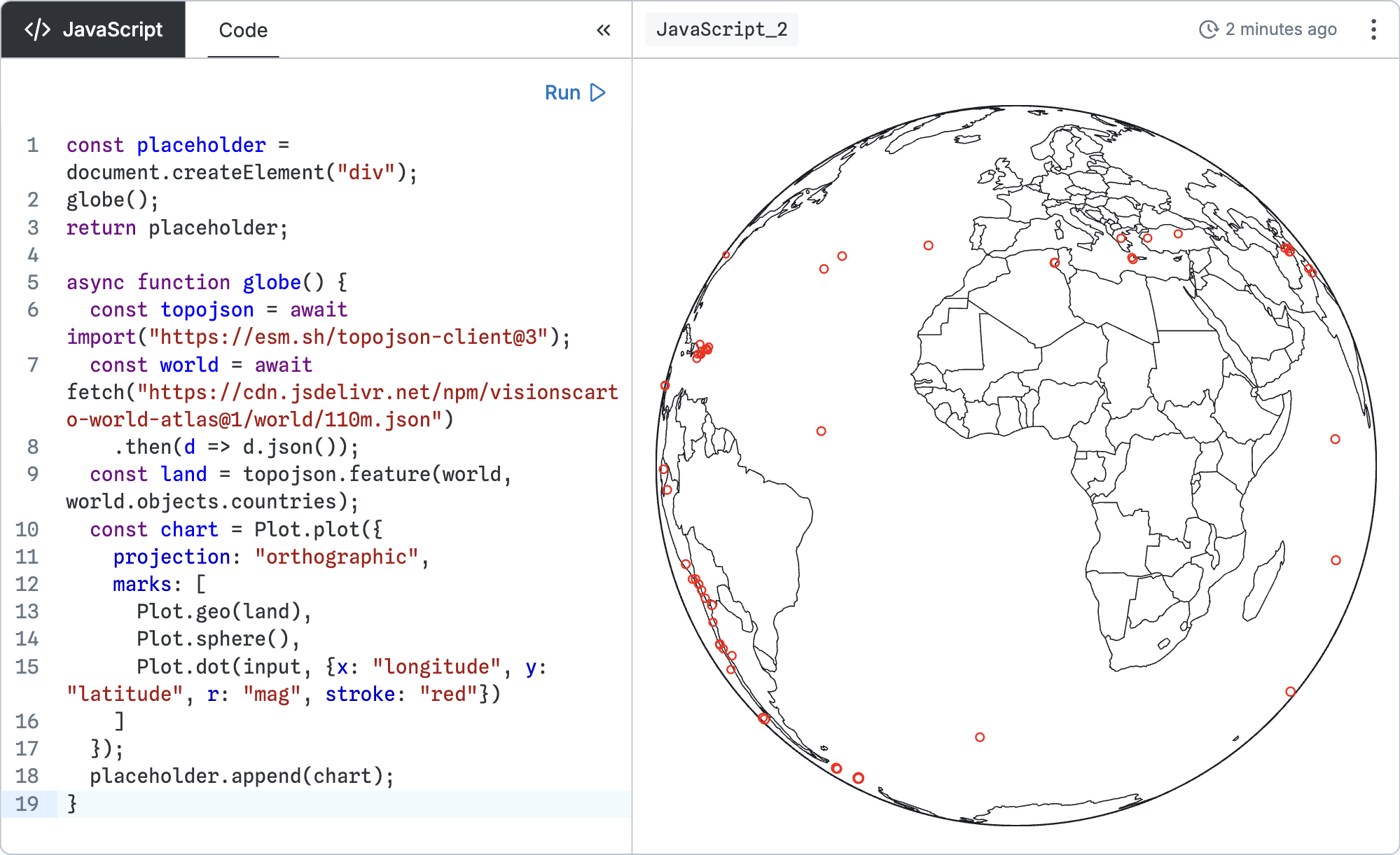
const placeholder = document.createElement("div");
globe();
return placeholder;
async function globe() {
const topojson = await import("https://esm.sh/topojson-client@3");
const world = await fetch("https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/visionscarto-world-atlas@1/world/110m.json")
.then(d => d.json());
const land = topojson.feature(world, world.objects.countries);
const chart = Plot.plot({
projection: "orthographic",
marks: [
Plot.geo(land),
Plot.sphere(),
Plot.dot(input, {x: "longitude", y: "latitude", r: "mag", stroke: "red"})
]
});
placeholder.append(chart);
}